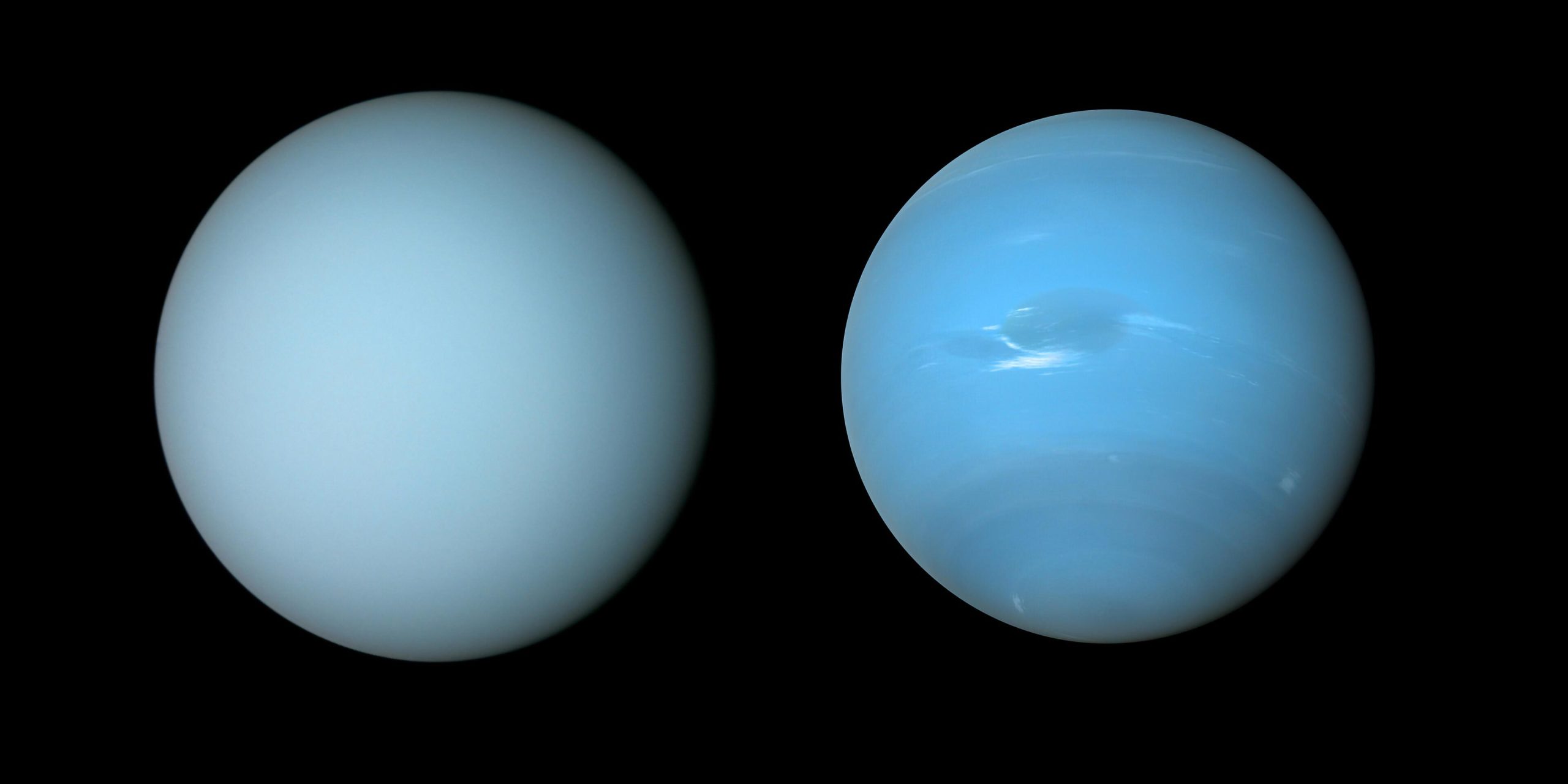

Космический корабль НАСА «Вояджер-2» запечатлел эти виды Урана (слева) и Нептуна (справа) во время облета планет в 1980-х годах. Авторы и права: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Б. Джонсон
Наблюдения с обсерватории Джемини и других телескопов показывают чрезмерную дымку.[{» attribute=»»>Uranus makes it paler than Neptune.
Astronomers may now understand why the similar planets Uranus and Neptune have distinctive hues. Researchers constructed a single atmospheric model that matches observations of both planets using observations from the Gemini North telescope, the NASA Infrared Telescope Facility, and the Hubble Space Telescope. The model reveals that excess haze on Uranus accumulates in the planet’s stagnant, sluggish atmosphere, giving it a lighter hue than Neptune.
Планеты Нептун и Уран имеют много общего — у них схожие массы, размеры и состав атмосферы — но их внешний вид заметно различается. В видимом диапазоне длин волн Нептун заметно голубее, а Уран имеет более бледный оттенок голубого. Теперь у астрономов есть объяснение, почему две планеты так отличаются по цвету.
Новое исследование показывает, что слой концентрированной дымки, обнаруженный на обеих планетах, на Уране толще, чем аналогичный слой на Нептуне, и «отбеливает» внешний вид Урана больше, чем на Нептуне.[1] Если нет тумана атмосфера От Нептуна и Урана они оба будут выглядеть примерно одинаково в синем цвете.[2]
Этот вывод следует из модели[3] которую международная группа под руководством Патрика Ирвина, профессора планетарной физики Оксфордского университета, разработала для описания аэрозольных слоев в атмосферах Нептуна и Урана.[4] Предыдущие исследования верхних атмосфер этих планет были сосредоточены на появлении атмосферы только на определенных длинах волн. Однако эта новая модель, состоящая из нескольких атмосферных слоев, соответствует наблюдениям с обеих планет в широком диапазоне длин волн. Новая модель также включает нечеткие частицы в более глубоких слоях, которые ранее считались содержащими только облака метана и сероводородного льда.

На этой диаграмме показаны три слоя аэрозолей в атмосферах Урана и Нептуна, разработанные группой ученых под руководством Патрика Ирвина. Альтиметр на графике показывает давление выше 10 бар.
Самый глубокий слой (аэрозольный слой-1) имеет большую толщину и состоит из смеси сероводородного льда и частиц от взаимодействия планетарных атмосфер с солнечным светом.
Основным слоем, влияющим на цвета, является средний слой, представляющий собой слой частиц тумана (называемый в статье аэрозольным слоем-2), который на Уране толще, чем на Нептуне. Команда подозревает, что на обеих планетах метановый лед конденсируется на частицах в этом слое, затягивая частицы глубже в атмосферу по мере выпадения метанового снега. Поскольку атмосфера Нептуна более активна и турбулентна, чем у Урана, команда считает, что атмосфера Нептуна более эффективна в перемещении частиц метана в слой дымки и производстве этого снега. Это удаляет больше дымки и делает слой дымки на Нептуне тоньше, чем на Уране, а это означает, что синий цвет Нептуна кажется более сильным.
Над обоими слоями находится расширенный слой тумана (аэрозольный слой 3), похожий на нижний слой, но более хрупкий. На Нептуне над этим слоем также образуются крупные частицы метанового льда.
Авторы и права: Международная обсерватория Близнецов/NOIRLab/NSF/AURA, Ж. да Силва/НАСА/Лаборатория реактивного движения-Калтех/Б. Джонсон
«Это первая модель, которая синхронно соответствует наблюдениям отраженного солнечного света от ультрафиолетового до ближнего инфракрасного», — пояснил Ирвин, ведущий автор исследовательской работы, представляющей это открытие в Журнале геофизических исследований: планеты. «Он также первым объяснил разницу в видимом цвете между Ураном и Нептуном».
Модель команды состоит из трех слоев аэрозолей на разных высотах.[5] Основным слоем, влияющим на цвета, является средний слой, представляющий собой слой частиц тумана (обозначаемый в документе как аэрозольный слой-2), который толще над Уран Принадлежащий Нептун. Команда подозревает, что на обеих планетах метановый лед конденсируется на частицах в этом слое, затягивая частицы глубже в атмосферу по мере выпадения метанового снега. Поскольку атмосфера Нептуна более активна и турбулентна, чем у Урана, команда считает, что атмосфера Нептуна более эффективна в перемещении частиц метана в слой дымки и производстве этого снега. Это удаляет больше дымки и делает слой дымки на Нептуне тоньше, чем на Уране, а это означает, что синий цвет Нептуна кажется более сильным.
Майк Вонг, астроном из[{» attribute=»»>University of California, Berkeley, and a member of the team behind this result. “Explaining the difference in color between Uranus and Neptune was an unexpected bonus!”
To create this model, Irwin’s team analyzed a set of observations of the planets encompassing ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared wavelengths (from 0.3 to 2.5 micrometers) taken with the Near-Infrared Integral Field Spectrometer (NIFS) on the Gemini North telescope near the summit of Maunakea in Hawai‘i — which is part of the international Gemini Observatory, a Program of NSF’s NOIRLab — as well as archival data from the NASA Infrared Telescope Facility, also located in Hawai‘i, and the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope.
The NIFS instrument on Gemini North was particularly important to this result as it is able to provide spectra — measurements of how bright an object is at different wavelengths — for every point in its field of view. This provided the team with detailed measurements of how reflective both planets’ atmospheres are across both the full disk of the planet and across a range of near-infrared wavelengths.
“The Gemini observatories continue to deliver new insights into the nature of our planetary neighbors,” said Martin Still, Gemini Program Officer at the National Science Foundation. “In this experiment, Gemini North provided a component within a suite of ground- and space-based facilities critical to the detection and characterization of atmospheric hazes.”
The model also helps explain the dark spots that are occasionally visible on Neptune and less commonly detected on Uranus. While astronomers were already aware of the presence of dark spots in the atmospheres of both planets, they didn’t know which aerosol layer was causing these dark spots or why the aerosols at those layers were less reflective. The team’s research sheds light on these questions by showing that a darkening of the deepest layer of their model would produce dark spots similar to those seen on Neptune and perhaps Uranus.
Notes
- This whitening effect is similar to how clouds in exoplanet atmospheres dull or ‘flatten’ features in the spectra of exoplanets.
- The red colors of the sunlight scattered from the haze and air molecules are more absorbed by methane molecules in the atmosphere of the planets. This process — referred to as Rayleigh scattering — is what makes skies blue here on Earth (though in Earth’s atmosphere sunlight is mostly scattered by nitrogen molecules rather than hydrogen molecules). Rayleigh scattering occurs predominantly at shorter, bluer wavelengths.
- An aerosol is a suspension of fine droplets or particles in a gas. Common examples on Earth include mist, soot, smoke, and fog. On Neptune and Uranus, particles produced by sunlight interacting with elements in the atmosphere (photochemical reactions) are responsible for aerosol hazes in these planets’ atmospheres.
- A scientific model is a computational tool used by scientists to test predictions about a phenomena that would be impossible to do in the real world.
- The deepest layer (referred to in the paper as the Aerosol-1 layer) is thick and is composed of a mixture of hydrogen sulfide ice and particles produced by the interaction of the planets’ atmospheres with sunlight. The top layer is an extended layer of haze (the Aerosol-3 layer) similar to the middle layer but more tenuous. On Neptune, large methane ice particles also form above this layer.
More information
This research was presented in the paper “Hazy blue worlds: A holistic aerosol model for Uranus and Neptune, including Dark Spots” to appear in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets.
The team is composed of P.G.J. Irwin (Department of Physics, University of Oxford, UK), N.A. Teanby (School of Earth Sciences, University of Bristol, UK), L.N. Fletcher (School of Physics & Astronomy, University of Leicester, UK), D. Toledo (Instituto Nacional de Tecnica Aeroespacial, Spain), G.S. Orton (Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, USA), M.H. Wong (Center for Integrative Planetary Science, University of California, Berkeley, USA), M.T. Roman (School of Physics & Astronomy, University of Leicester, UK), S. Perez-Hoyos (University of the Basque Country, Spain), A. James (Department of Physics, University of Oxford, UK), J. Dobinson (Department of Physics, University of Oxford, UK).
NSF’s NOIRLab (National Optical-Infrared Astronomy Research Laboratory), the US center for ground-based optical-infrared astronomy, operates the international Gemini Observatory (a facility of NSF, NRC–Canada, ANID–Chile, MCTIC–Brazil, MINCyT–Argentina, and KASI–Republic of Korea), Kitt Peak National Observatory (KPNO), Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (CTIO), the Community Science and Data Center (CSDC), and Vera C. Rubin Observatory (operated in cooperation with the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory). It is managed by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy (AURA) under a cooperative agreement with NSF and is headquartered in Tucson, Arizona. The astronomical community is honored to have the opportunity to conduct astronomical research on Iolkam Du’ag (Kitt Peak) in Arizona, on Maunakea in Hawai‘i, and on Cerro Tololo and Cerro Pachón in Chile. We recognize and acknowledge the very significant cultural role and reverence that these sites have for the Tohono O’odham Nation, the Native Hawaiian community, and the local communities in Chile, respectively.

«Интроверт. Мыслитель. Решатель проблем. Злой специалист по пиву. Склонен к приступам апатии. Эксперт по социальным сетям».





More Stories
Астронавт НАСА публикует фотографию Луны над Тихим океаном: «Удивительно»
Компенсация сна по выходным может снизить риск сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний на пятую часть — исследование | Сердечное заболевание
Согласно окаменелостям, доисторическую морскую корову съели крокодил и акула